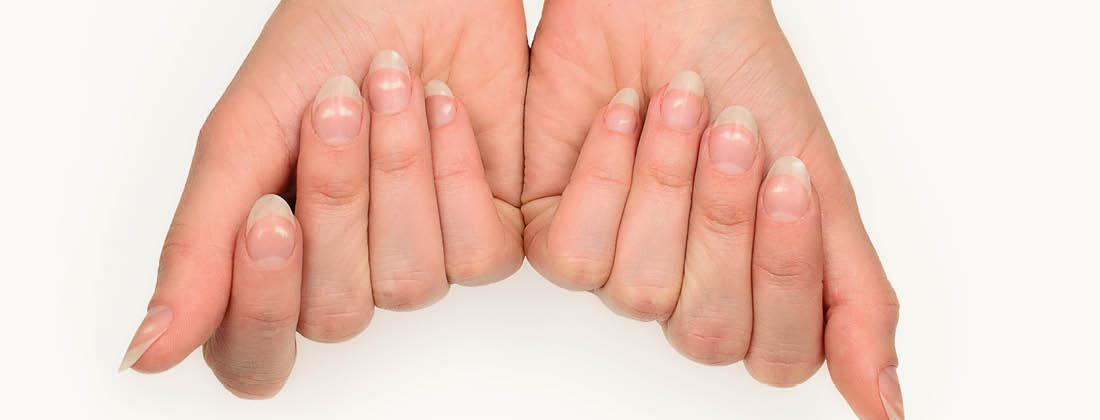
What are those white spots on your nails?
As a naturopath I am often asked by people what the white spots on their nails are caused by. Most people think this is calcium deficiency. The clever answer is that it is called Leukonychia (pronounced Loo-co-ni-kia) and you can see a fine example in the picture here. The main cause of white dots on fingernails, other than physical injury like shutting your finger in something, is zinc deficiency. What is zinc deficiency? It's a common deficiency as zinc is extensively used in the body and is short in NZ soils.
So what is zinc?
As you can guess being in the soil, zinc is a mineral. It’s found abundantly in the body, mainly in the muscles and bones. However, it’s also found in the teeth, hair, skin, nails, liver, prostate, testes, sperm and in our white blood cells. It is used in over 100 important activities in our body, which makes it one of our key nutrients.
What is it used for?
Zinc is required for healthy building and repair in the body. It's important for healthy hair, nails and skin growth. Hence when there is lack of zinc there can be slow healing, and white spots on nails. It is also important for healthy bone formation and is used to make the hormone called calcitonin which helps maintain balanced calcium in the blood.
It is very important for the immune system, so people who are lacking often seem to catch one thing after another. There are studies that show taking zinc cans support healthy recovery from ills and chills. Zinc is used by the body in the saliva as the first line of defence as part of normal digestive immune function.
Zinc is also needed for reproductive health as it is required for s healthy sex hormones for all genders. It is very important for male sexual, reproductive and prostate health. Other hormones which need zinc are growth hormones and insulin for healthy growth and healthy blood sugar levels. Finally, zinc is used in the production of thyroid hormones, so healthy zinc levels support a normal metabolism.
Signs of Zinc Deficiency
There are many signs of zinc deficiency, but the main ones (other than white spots on fingernails) are stretch marks, thinning hair, blemishes, slow healing, bowel changes, getting sick more often, and scaly scalp.Those who are lacking zinc may also have poor taste, poor smell and experience loss of appetite. So think of zinc with your kids if they don’t seem interested in eating, especially if they often come down with ills and chills.
Who might be susceptible to zinc deficiency?
- Those who sweat a lot or do intense exercise
- People taking medications – for example the oral contraceptive, antacids and antibiotics
- Digestive disorders that result in lack of absorption
- Those with high intakes of caffeine and alcohol
- People who are under stress
- Diabetics and those with liver or kidney issues
- During and after pregnancy (It can also support healthy mood along with Vitamin B6).
- Teenagers as they are growing and developing sex hormones
- Growing kids
- Vegans or vegetarians due to the high consumption of foods such as wholegrains, rice, corn and legumes. These are high in phytates that can block zinc absorption. Zinc is also commonly found in animal proteins which are not consumed.
Are there any vitamins or minerals that can affect zinc absorption?
Zinc competes for absorption with iron, copper and calcium.
Foods that contain zinc
Zinc is naturally present in food such as meat, poultry, dairy products, eggs, fish, beans, and nuts. It is very high in oysters, and other good sources include pumpkin and sunflower seeds which are great toasted - they’re super affordable and tasty to throw on your salads. For vegetarians, kelp and spirulina are great sources.
Are you Zinc deficient?
There are tests for zinc deficiency. You can measure levels by a blood test through your GP.
Recommended daily intake according to the NZ Ministry of Health
| 7 months – 3 years | 3mg | |
| 4 -8 years | 4mg | |
| 9 – 13 years | 6mg | |
| 14 – 18 years (girls) | 7mg | |
| 14 – 18 years (boys) |
|
13mg |
| Men | 14mg | |
| Women | 8mg | |
| Pregnancy | 11mg | |
| Breastfeeding | 12mg |
Clinicians Zinc Oral Drops provide 5mg of Zinc (as Zinc Sulfate) per 5 drops. Liquid form provides greater absorption and assimilation.